The main differences between antique lamp bulbs and modern ones revolve around their design, materials, and functionality:
Filament Design:
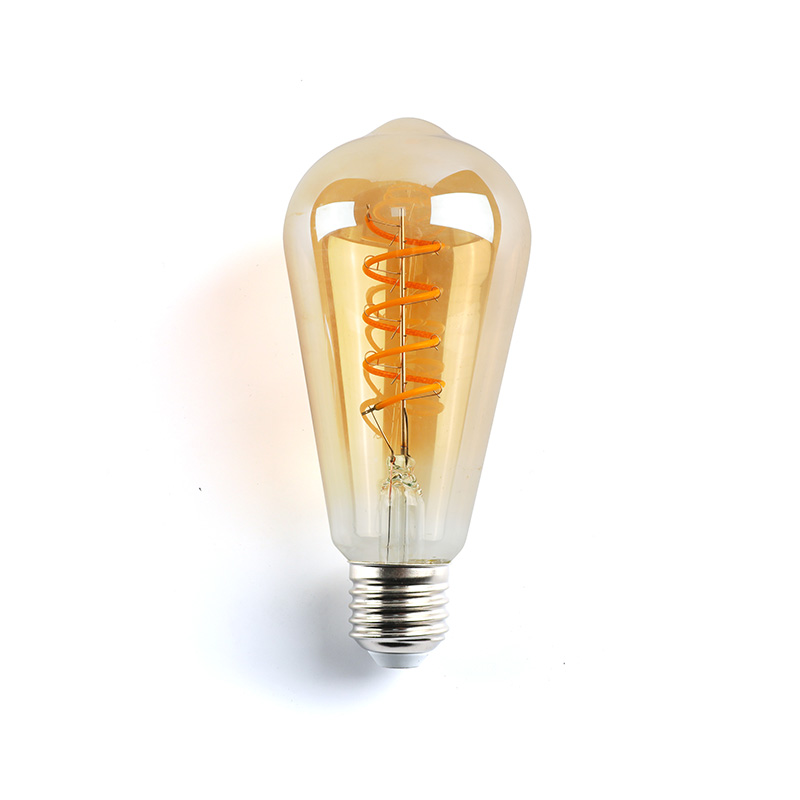
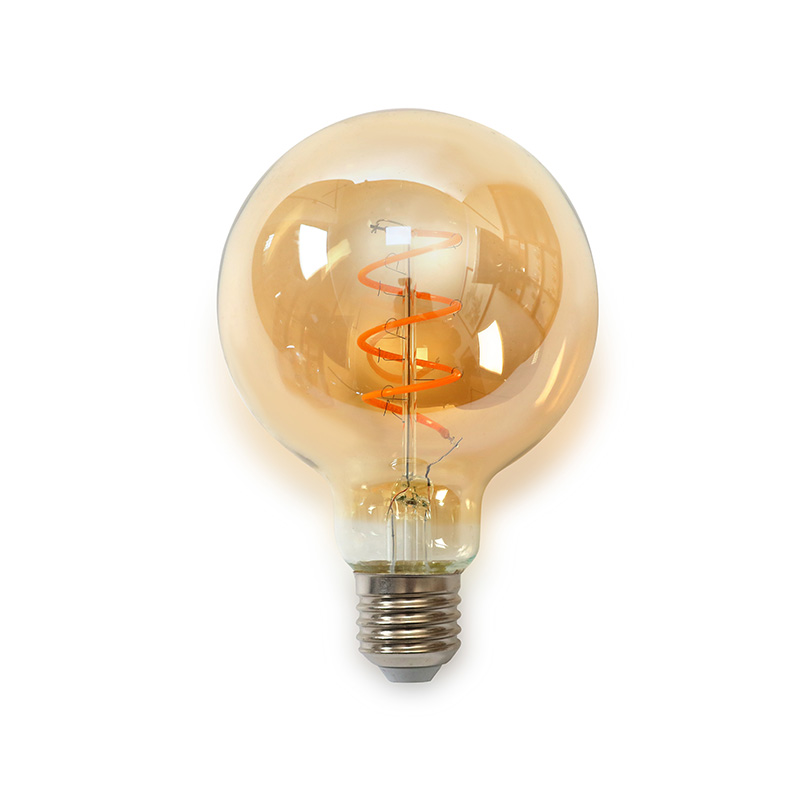
Antique Bulbs: Early lamp bulbs, such as carbon or tungsten filament bulbs, often feature long, exposed filaments that produce a warm, soft glow. The filaments are intricately coiled and visible, giving the bulb a decorative and vintage aesthetic.
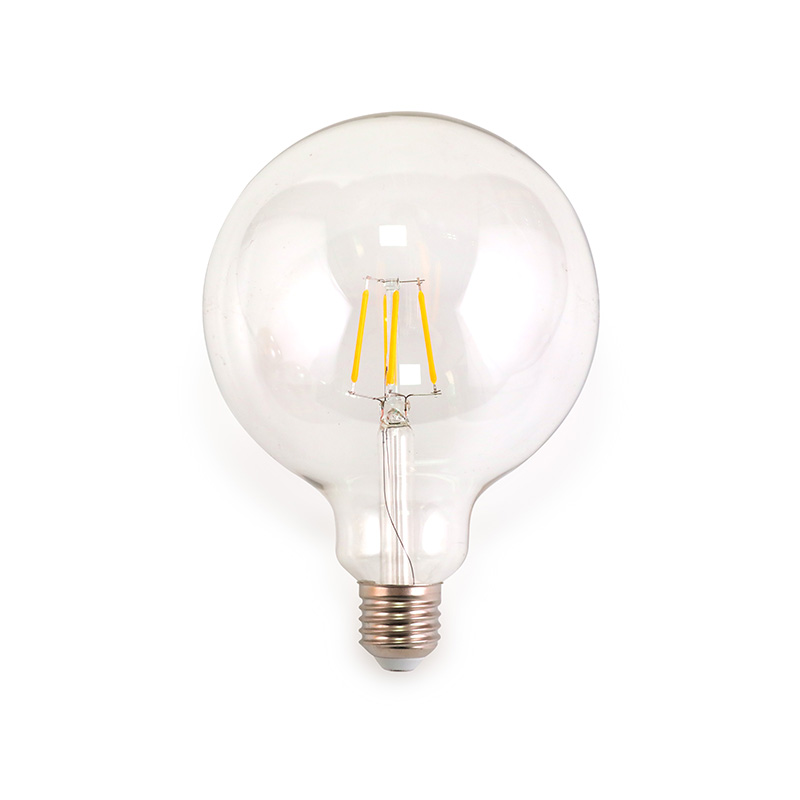
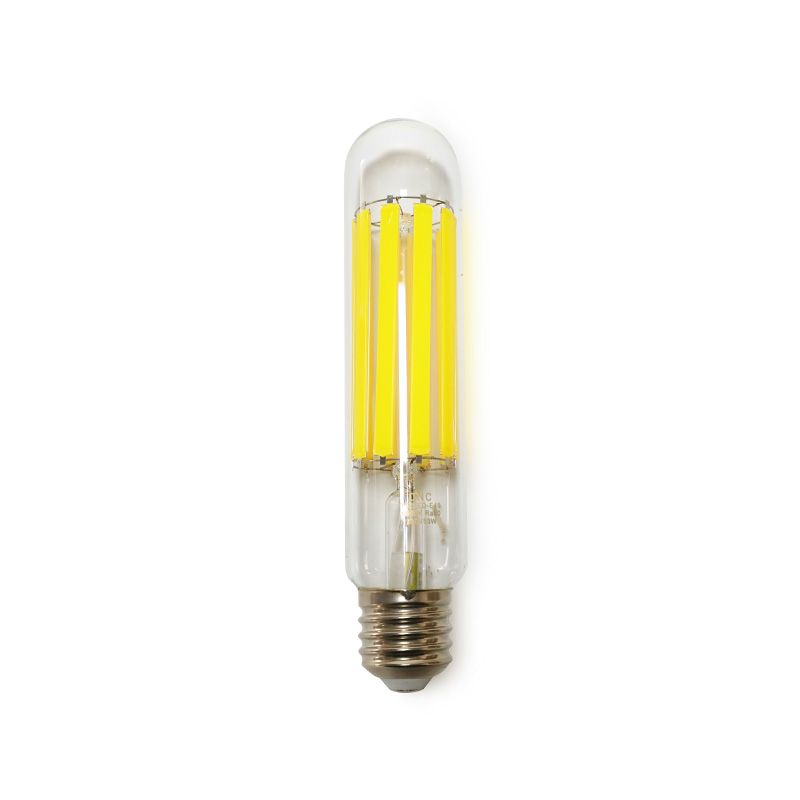
Modern Bulbs: Modern bulbs, particularly LED and CFL bulbs, use advanced technology with no visible filaments. The design is more functional and energy-efficient, focusing on light output rather than aesthetic.
Materials:
Antique Bulbs: Typically made with carbon or tungsten filaments, glass casings are often hand-blown or thicker, giving the bulbs a more fragile, vintage feel. Many also feature brass or porcelain bases.
Modern Bulbs: Modern materials include plastic and lighter-weight glass, often with more durable metal bases and LED chips rather than filaments.
Light Quality:
Antique Bulbs: Produce a warm, amber light, which is softer and more diffuse due to the lower efficiency and technology of the time.
Modern Bulbs: Offer a wide range of color temperatures, from warm to cool, and can be far brighter with significantly better energy efficiency.

Energy Efficiency:
Antique Bulbs: These bulbs are highly inefficient, converting most energy into heat rather than light. For instance, early Edison bulbs or carbon filament bulbs are known for their low lumen output per watt.
Modern Bulbs: LEDs, CFLs, and even modern incandescent bulbs are designed to be energy efficient, using far less electricity to produce much more light and generating less heat.
Longevity:
Antique Bulbs: The lifespan of antique bulbs is generally shorter due to their fragile filaments and the lower efficiency of materials.
Modern Bulbs: LEDs and other modern bulb types can last tens of thousands of hours, requiring less frequent replacement.
Design Purpose:
Antique Bulbs: Initially designed for functionality but evolved into decorative pieces. They are now often used for their nostalgic appeal, especially in retro or industrial-style decor.
Modern Bulbs: Designed primarily for energy efficiency, sustainability, and performance, often focusing on smart lighting features such as dimming, color control, and automation.
Heat Emission:
Antique Bulbs: Emit a significant amount of heat as a byproduct of light production.
Modern Bulbs: Emit very little heat, particularly LED bulbs, which remain cool to the touch even after long periods of use.
While antique bulbs are celebrated for their aesthetic appeal and nostalgic design, modern bulbs are valued for their energy efficiency, long life, and advanced functionalities.

 English
English русский
русский